Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitamura, Akira; *
JNC TN8400 2001-009, 54 Pages, 2001/01
Spectroscopic measurements of neodymium(III) and samarium(III) were carried out by spectrophotometer and laser-induced photoacoustic spectroscopic (LPAS) system for the investigation of the detection limit of both systems. The absorption spectra and photoacoustic spectra of Nd and Sm
and Sm were obtained with varying the concentration of the ions from 2
were obtained with varying the concentration of the ions from 2 10
10 to 2
to 2 10
10 mol
mol dm
dm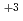 . The absorption spectrum of Nd
. The absorption spectrum of Nd was also determined by a special spectrophotometer, of which the measurement cell was set in a glove box filled with inert nitrogen gas. For the comparison with these photoacoustic and absorption spectra, the absorption spectra of Nd
was also determined by a special spectrophotometer, of which the measurement cell was set in a glove box filled with inert nitrogen gas. For the comparison with these photoacoustic and absorption spectra, the absorption spectra of Nd and Sm
and Sm were determined by an usual spectrophotometer with the light-path lengths of 1 cm and 10 cm. The detection limit of the photoacoustic measurement was reported much lower than that of absorbance measurement by several researchers. However, the present study was concluded that the detection limit of photoacoustic measurement with the present LPAS system was similar to that of absorbance measurement with the light-path length of 10 cm. The detection limits of neptunium(IV,V) were estimated and the possibility of the speciation of neptunium(IV) was discussed from the results of the present study.
were determined by an usual spectrophotometer with the light-path lengths of 1 cm and 10 cm. The detection limit of the photoacoustic measurement was reported much lower than that of absorbance measurement by several researchers. However, the present study was concluded that the detection limit of photoacoustic measurement with the present LPAS system was similar to that of absorbance measurement with the light-path length of 10 cm. The detection limits of neptunium(IV,V) were estimated and the possibility of the speciation of neptunium(IV) was discussed from the results of the present study.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Aoyagi, Noboru
no journal, ,
Although carrier-free radiotracers are utilized in lots of research fields, their chemical forms have not been identified by UV/vis. spectroscopy because of their micro quantities. In this study, we are developing an apparatus for cavity ring-down spectroscopy to perform absorption spectroscopy of radioiodine and astatine in a gas-phase. With this apparatus, ultra-sensitive absorption measurement is realized by making injected pulse-laser go back and forth tens of thousand times between facing mirrors. Intensity of laser in the cavity becomes weaker by its escaping through the mirrors and by absorption by samples. Absorption coefficients are obtained from difference in the life-time of escaped light between blank and sample measurements. Chemical species are expected to be characterized by measuring absorption coefficients at various wavelength and comparing these with known spectra and theoretical calculations. In the symposium, present status of the development will be reported.